Online first
Current issue
Archive
Special Issues
About the Journal
Publication Ethics
Anti-Plagiarism system
Instructions for Authors
Instructions for Reviewers
Editorial Board
Editorial Office
Contact
Reviewers
All Reviewers
2025
2024
2023
2022
2021
2020
2019
2018
2017
2016
General Data Protection Regulation (RODO)
RESEARCH PAPER
Clinical significance of serum ATP8B1 in children with Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection complicated with myocardial injury
1
Department of Paediatrics, Tangshan Central Hospital, Tangshan, China
These authors had equal contribution to this work
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction and objective:
Mycoplasma pneumoniae (MP) infection can lead to various extrapulmonary complications, including myocardial injury (MI). However, the expression levels of ATPase phospholipid transporting 8B1 (ATP8B1) in MP-infected individuals with MI and its potential therapeutic role remain elusive. The aim of the study is to evaluate ATP8B1 as a therapeutic target for MP-induced MI.
Material and methods:
The study quantified ATP8B1 expression in patient serum via RT-qPCR and analyzed its diagnostic value for MP and MP+MI using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves. Binary logistic regression assessed its association with MP+MI. Serum interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) levels were measured by ELISA and correlated with ATP8B1. In a dual-cell model (MP-infected BEAS-2B cells and AC16 cells exposed to their supernatant), ATP8B1’s effects on inflammation, proliferation, reactive oxygen species (ROS), and cardiac injury markers were evaluated via RT-qPCR, CCK-8, and ELISA.
Results:
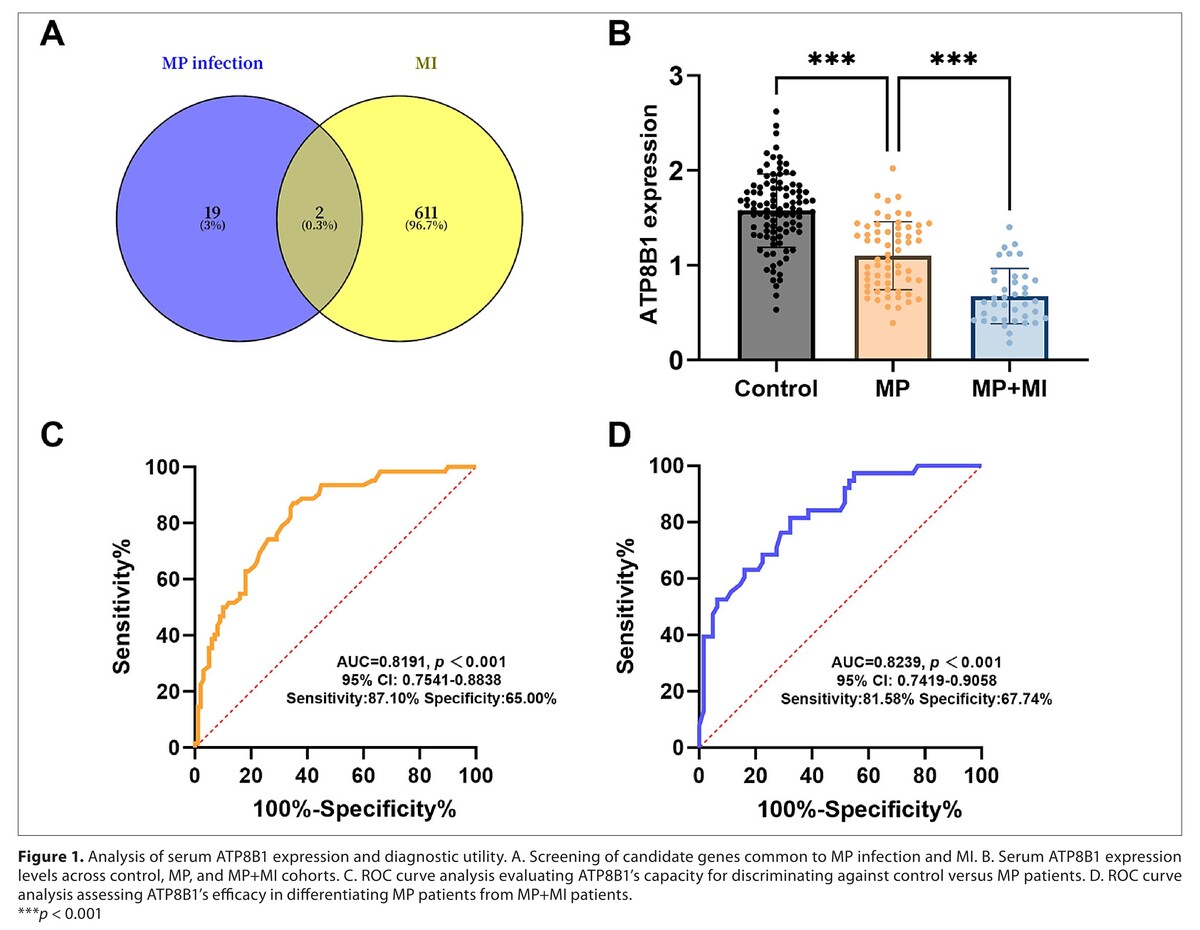
The study revealed that serum ATP8B1 levels were significantly reduced in the MP group and further decreased in the MP+MI group. ATP8B1 expression levels could distinguish MP patients from MP+MI patients. Serum IL-6 and TNF-α levels were significantly higher in the MP+MI group than in the MP group, and ATP8B1 was negatively correlated with IL-6 and TNF-α. In vitro, ATP8B1 was downregulated in both cell lines. Functionally, over-expression of ATP8B1 effectively attenuated inflammation, ROS production, deficits in cell proliferation, and myocardial injury.
Conclusions:
ATP8B1 was expressed lowly in the serum of MP+MI patients. Functional experiments demonstrated that ATP8B1 upregulation significantly attenuated inflammation, ROS generation, proliferation deficits, and myocardial injury.
Mycoplasma pneumoniae (MP) infection can lead to various extrapulmonary complications, including myocardial injury (MI). However, the expression levels of ATPase phospholipid transporting 8B1 (ATP8B1) in MP-infected individuals with MI and its potential therapeutic role remain elusive. The aim of the study is to evaluate ATP8B1 as a therapeutic target for MP-induced MI.
Material and methods:
The study quantified ATP8B1 expression in patient serum via RT-qPCR and analyzed its diagnostic value for MP and MP+MI using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves. Binary logistic regression assessed its association with MP+MI. Serum interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) levels were measured by ELISA and correlated with ATP8B1. In a dual-cell model (MP-infected BEAS-2B cells and AC16 cells exposed to their supernatant), ATP8B1’s effects on inflammation, proliferation, reactive oxygen species (ROS), and cardiac injury markers were evaluated via RT-qPCR, CCK-8, and ELISA.
Results:
The study revealed that serum ATP8B1 levels were significantly reduced in the MP group and further decreased in the MP+MI group. ATP8B1 expression levels could distinguish MP patients from MP+MI patients. Serum IL-6 and TNF-α levels were significantly higher in the MP+MI group than in the MP group, and ATP8B1 was negatively correlated with IL-6 and TNF-α. In vitro, ATP8B1 was downregulated in both cell lines. Functionally, over-expression of ATP8B1 effectively attenuated inflammation, ROS production, deficits in cell proliferation, and myocardial injury.
Conclusions:
ATP8B1 was expressed lowly in the serum of MP+MI patients. Functional experiments demonstrated that ATP8B1 upregulation significantly attenuated inflammation, ROS generation, proliferation deficits, and myocardial injury.
REFERENCES (23)
1.
Kumar S. Mycoplasma pneumoniae: A significant but underrated pathogen in paediatric community-acquired lower respiratory tract infections. Indian J Med Res. 2018;147(1):23–31.
2.
Kutty PK, Jain S, Taylor TH, et al. Mycoplasma pneumoniae Among Children Hospitalized With Community-acquired Pneumonia. Clin Infect Dis. 2019;68(1):5–12.
3.
Li M, Lu L, Xu H. Diagnostic value of miR-34a in Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children and its correlation with rehabilitation effect. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2024;19(1):507.
4.
Gao L, Sun Y. Laboratory diagnosis and treatment of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in children: a review. Ann Med. 2024;56(1):2386636.
5.
Balac N, Nelson KF, Naib T, et al. The chicken or the egg? Mycoplasma pneumoniae complicated by left ventricle thrombus and anterior myocardial infarction: a case report. Eur Heart J Case Rep. 2024;8(9):ytae434.
6.
Ponka A. Carditis associated with mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Acta Med Scand. 1979;206(1–2):77–86.
7.
Lu G, Li X, Tang J, et al. Mycoplasma infection aggravates cardiac involvements in Kawasaki diseases: a retrospective study. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1310134.
8.
Tamura R, Sabu Y, Mizuno T, et al. Intestinal Atp8b1 dysfunction causes hepatic choline deficiency and steatohepatitis. Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):6763.
9.
Althenayyan S, AlGhamdi A, AlMuhanna MH, et al. Modulation of ATP8B1 Gene Expression in Colorectal Cancer Cells Suggest its Role as a Tumor Suppressor. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2022;22(7):577–90.
10.
Zhang X, Zhang R, Liu P, et al. ATP8B1 Knockdown Activated the Choline Metabolism Pathway and Induced High-Level Intracellular REDOX Homeostasis in Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers (Basel). 2022;14(3).
11.
Fukumoto J, Leung J, Cox R, et al. Oxidative stress induces club cell proliferation and pulmonary fibrosis in Atp8b1 mutant mice. Aging (Albany NY). 2019;11(1):209–29.
12.
Lachat J, Pascault A, Thibaut D, et al. Trans-cellular tunnels induced by the fungal pathogen Candida albicans facilitate invasion through successive epithelial cells without host damage. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):3781.
13.
Waites KB, Crabb DM, Bing X, Duffy LB. In vitro susceptibilities to and bactericidal activities of garenoxacin (BMS-284756) and other antimicrobial agents against human mycoplasmas and ureaplasmas. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003;47(1):161–5.
14.
Wang YS, Zhou YL, Bai GN, et al. Expert consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children. World J Pediatr. 2024;20(9):901–14.
15.
Wang Y, Ma C, Hao X, et al. Identification of Mycoplasma pneumoniae proteins interacting with NOD2 and their role in macrophage inflammatory response. Front Microbiol. 2024;15:1391453.
16.
Kariya C, Chu HW, Huang J, et al. Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection and environmental tobacco smoke inhibit lung glutathione adaptive responses and increase oxidative stress. Infect Immun. 2008;76(10):4455–62.
17.
Meduri GU, Annane D, Chrousos GP, Marik PE, Sinclair SE. Activation and regulation of systemic inflammation in ARDS: rationale for prolonged glucocorticoid therapy. Chest. 2009;136(6):1631–43.
18.
Ziaka M, Exadaktylos A. ARDS associated acute brain injury: from the lung to the brain. Eur J Med Res. 2022;27(1):150.
19.
Ji Y, Karbaschi M, Cooke MS. Mycoplasma infection of cultured cells induces oxidative stress and attenuates cellular base excision repair activity. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2019;845:403054.
20.
Yang WJ, Cao RC, Xiao W, et al. Correction: Acinar ATP8b1/LPC pathway promotes macrophage efferocytosis and clearance of inflammation during chronic pancreatitis development. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(11):930.
21.
Chen LC, Huang SP, Shih CT, et al. ATP8B1: A prognostic prostate cancer biomarker identified via genetic analysis. Prostate. 2023;83(6):602–11.
22.
Myo YPA, Camus SV, Freeberg MAT, et al. Protocol for differentiating primary human small airway epithelial cells at the air-liquid interface. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2025;328(6):L757–L71.
23.
Onodi Z, Visnovitz T, Kiss B, et al. Systematic transcriptomic and phenotypic characterization of human and murine cardiac myocyte cell lines and primary cardiomyocytes reveals serious limitations and low resemblances to adult cardiac phenotype. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2022;165:19–30.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.