Online first
Current issue
Archive
Special Issues
About the Journal
Publication Ethics
Anti-Plagiarism system
Instructions for Authors
Instructions for Reviewers
Editorial Board
Editorial Office
Contact
Reviewers
All Reviewers
2025
2024
2023
2022
2021
2020
2019
2018
2017
2016
General Data Protection Regulation (RODO)
RESEARCH PAPER
OLMALINC alleviates dexamethasone-induced osteoporosis via targeting miR-124-3p
1
Anesthesiology, The Wuhan Hospital of TCM Affiliated to Hubei University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Wuhan, China
2
Endocrinology, Wuhan No.9 Hospital, Wuhan, China
3
Orthopedics, The Wuhan Hospital of TCM Affiliated to Hubei University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Wuhan, China
These authors had equal contribution to this work
Corresponding author
Huan Yang
Orthopedics, The Wuhan Hospital of TCM Affiliated to Hubei University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, China
Orthopedics, The Wuhan Hospital of TCM Affiliated to Hubei University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, China
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction and objective:
This study aims to investigate the mechanism of LncRNA(lncRNAs) OLMALINC in dexamethasone (Dex)-induced osteoblast differentiation impairment and osteoporosis.
Material and methods:
To investigate the impact of OLMALINC and miR-124-3p on Dex-treated osteoblasts, functional gain and loss experiments were conducted using MC3T3-E1 cells. Dual-luciferase reporter assays, RNA pull-down, and MS-RIP experiments were used to verify the targeting relationship between OLMALINC and miR-124-3p. RT-qPCR was conducted to analyze OLMALINC and miR-124-3p levels, as well as osteogenic regulatory factors OPG, Runx2, and ALP-related mRNA in different treatment groups. Protein expression levels were determined by Western blot analysis. Apoptosis was assessed by flow cytometry. cell viability was assessed by CCK-8.
Results:
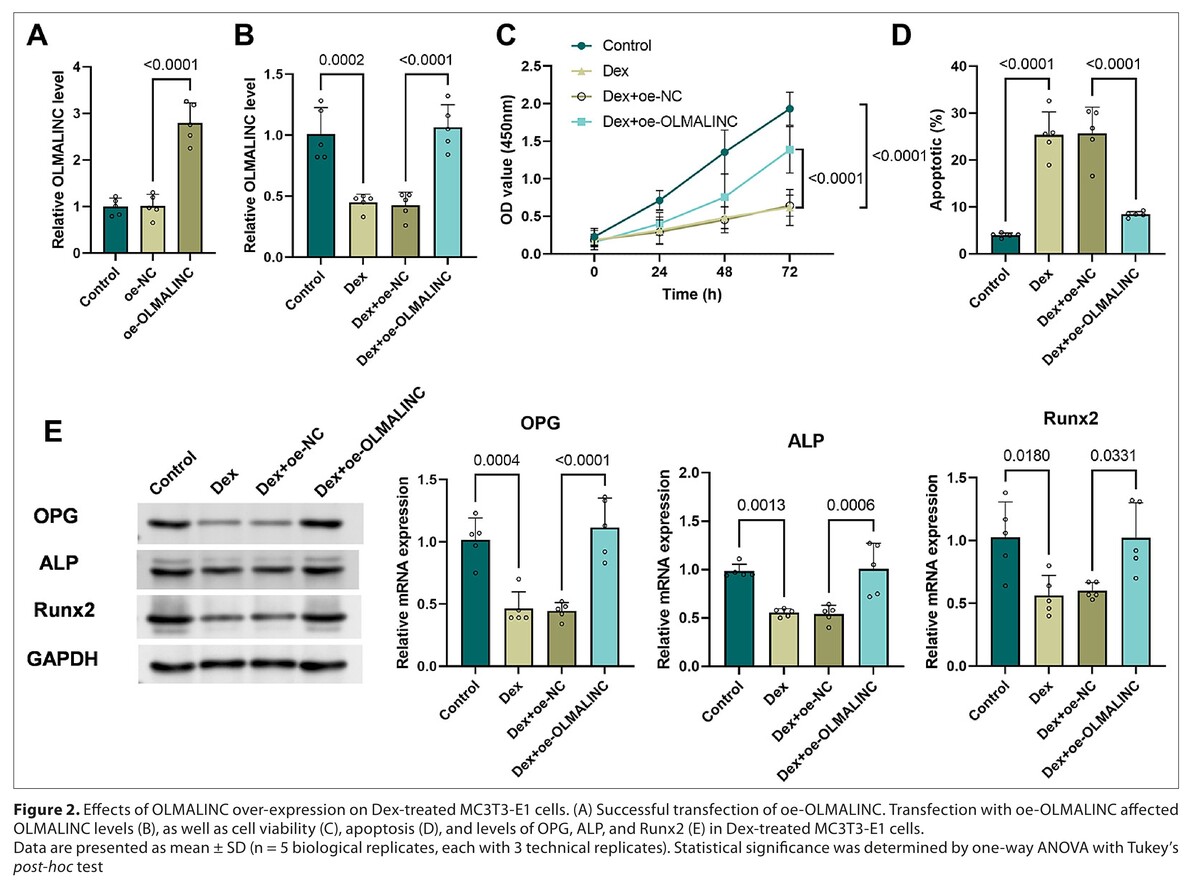
After Dex treatment, OLMALINC levels decreased, while miR-124-3p increased. Transfection of oe-OLMALINC counteracted Dex-induced osteogenic damage by increasing cell viability, decreasing apoptosis reduction, stimulating OPG, ALP, and Runx2 stimulation. OLMALINC targeted miR-124-3p, with OLMALINC negatively regulating miR-124-3p. In turn, miR-124-3p mimic reversed the protective effect of OLMALINC against Dex-induced osteoblast dysfunction.
Conclusions:
These results indicate that the OLMALINC/miR-124-3p axis influences osteoblast differentiation in Dex-induced osteoblast differentiation impairment and osteoporosis by regulating cell viability, apoptosis, and osteogenic factors.
This study aims to investigate the mechanism of LncRNA(lncRNAs) OLMALINC in dexamethasone (Dex)-induced osteoblast differentiation impairment and osteoporosis.
Material and methods:
To investigate the impact of OLMALINC and miR-124-3p on Dex-treated osteoblasts, functional gain and loss experiments were conducted using MC3T3-E1 cells. Dual-luciferase reporter assays, RNA pull-down, and MS-RIP experiments were used to verify the targeting relationship between OLMALINC and miR-124-3p. RT-qPCR was conducted to analyze OLMALINC and miR-124-3p levels, as well as osteogenic regulatory factors OPG, Runx2, and ALP-related mRNA in different treatment groups. Protein expression levels were determined by Western blot analysis. Apoptosis was assessed by flow cytometry. cell viability was assessed by CCK-8.
Results:
After Dex treatment, OLMALINC levels decreased, while miR-124-3p increased. Transfection of oe-OLMALINC counteracted Dex-induced osteogenic damage by increasing cell viability, decreasing apoptosis reduction, stimulating OPG, ALP, and Runx2 stimulation. OLMALINC targeted miR-124-3p, with OLMALINC negatively regulating miR-124-3p. In turn, miR-124-3p mimic reversed the protective effect of OLMALINC against Dex-induced osteoblast dysfunction.
Conclusions:
These results indicate that the OLMALINC/miR-124-3p axis influences osteoblast differentiation in Dex-induced osteoblast differentiation impairment and osteoporosis by regulating cell viability, apoptosis, and osteogenic factors.
REFERENCES (31)
1.
Figliomeni A, Signorini V, Mazzantini M. One year in review 2018: progress in osteoporosis treatment. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2018;36(6):948–58.
2.
Lis-Studniarska D, Studniarski M, Zakrzewska A, et al. Determining the hierarchy of risk factors for low-energy fractures in patients of an Osteoporosis Treatment Clinic. Ann Agric Environ Med. 2024;31(3):401–9.
3.
Chen Y, Sun Y, Xue X, et al. Comprehensive analysis of epigenetics mechanisms in osteoporosis. Front Genet. 2023;14:1153585.
4.
Paglialunga M, Flamini S, Contini R, et al. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Synthetic Peptides Based on Glucocorticoid-Induced Leucine Zipper (GILZ) Protein for the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (IBDs). Cells. 2023;12(18).
5.
Xiao J, Li W, Li G, et al. STK11 overexpression prevents glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis via activating the AMPK/SIRT1/PGC1alpha axis. Hum Cell. 2022;35(4):1045–59.
6.
Han X, Bai F, Li P, et al. Identification of novel potential drugs for the treatment and prevention of osteoarthritis. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2024;37:101647.
7.
Szudy-Szczyrek A, Chocholska S, Bachanek-Mitura O, et al. Efficacy of ixazomib-lenalidomide-dexamethasone in high-molecular-riskrelapsed/refractory multiple myeloma – case series and literature review. Ann Agric Environ Med. 2022;29(1):103–9.
8.
Mitra R. Adverse effects of corticosteroids on bone metabolism: a review. PM R. 2011;3(5):466–71; quiz 71.
9.
Zheng X, Ye FC, Sun T, et al. Delay the progression of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis: Fraxin targets ferroptosis via the Nrf2/GPX4 pathway. Phytother Res. 2024;38(11):5203–24.
10.
Fan H, Zhou Y, Zhang Z, et al. ROR1-AS1: A Meaningful Long Noncoding RNA in Oncogenesis. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2024;24(21):1884–93.
11.
Baniasadi M, Talebi S, Mokhtari K, et al. Role of non-coding RNAs in osteoporosis. Pathol Res Pract. 2024;253:155036.
12.
Zhao Y, Ning J, Teng H, et al. Long noncoding RNA Malat1 protects against osteoporosis and bone metastasis. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):2384.
13.
Yang Y, Yujiao W, Fang W, et al. The roles of miRNA, lncRNA and circRNA in the development of osteoporosis. Biol Res. 2020;53(1):40.
14.
Shuai ZQ, Wang ZX, Ren JL, et al. Differential expressions and potential clinical values of lncRNAs in the plasma exosomes of rheumatoid arthritis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024;128:111511.
15.
Zhang M, Cheng L, Zhang Y. Characterization of Dysregulated lncRNA-Associated ceRNA Network Reveals Novel lncRNAs With ceRNA Activity as Epigenetic Diagnostic Biomarkers for Osteoporosis Risk. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:184.
16.
He Y, Zhou H, Xu H, et al. Construction of an Immune-Related lncRNA Signature That Predicts Prognosis and Immune Microenvironment in Osteosarcoma Patients. Front Oncol. 2022;12:769202.
17.
Dai X, Liu C, Bi W, et al. Estradiol and vitamin D exert a synergistic effect on preventing osteoporosis via the miR-351-5p/IRS1 axis and mTOR/NFkappaB signaling pathway. Sci Rep. 2025;15(1):18678.
18.
Wang N, Wang H, Chen J, et al. ACY-1215, a HDAC6 inhibitor, decreases the dexamethasone-induced suppression of osteogenesis in MC3T3-E1 cells. Mol Med Rep. 2020;22(3):2451–9.
19.
Lee S, Kim M, Hong S, et al. Effects of Sparganii Rhizoma on Osteoclast Formation and Osteoblast Differentiation and on an OVX-Induced Bone Loss Model. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:797892.
20.
Zhan W, Ruan B, Dong H, et al. Isopsoralen suppresses receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-beta ligand-induced osteoclastogenesis by inhibiting the NF-kappaB signaling. PeerJ. 2023;11:e14560.
21.
Kaczmarczyk-Sedlak I, Wojnar W, Zych M, et al. Effect of formononetin on mechanical properties and chemical composition of bones in rats with ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:457052.
22.
Ille M, Matic S, Gambiroza K, et al. Assessment of post-traumatic arthritis and functional outcome in patients treated operatively and non-operatively for distal radius Fractures – a 2-year cohort study. Ann Agric Environ Med. 2025;32(2):288–94.
23.
Zhang H, Wei W, Qian B, et al. Screening for osteoporosis based on IQon spectral CT virtual low monoenergetic images: Comparison with conventional 120 kVp images. Heliyon. 2023;9(10):e20750.
24.
Nemeth K, Bayraktar R, Ferracin M, et al. Non-coding RNAs in disease: from mechanisms to therapeutics. Nat Rev Genet. 2024;25(3):211–32.
25.
Wang G, Lee-Yow Y, Chang HY. Approaches to probe and perturb long noncoding RNA functions in diseases. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2024;85:102158.
26.
Li B, Wang J, Xu F, et al. LncRNA RAD51-AS1 Regulates Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells via Interaction with YBX1 to Ameliorate Osteoporosis. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2023;19(1):170–87.
27.
Zhu Z, Huang F, Jiang Y, et al. OLMALINC/OCT4/BMP2 axis enhances osteogenic-like phenotype of renal interstitial fibroblasts to participate in Randall’s plaque formation. Mol Med. 2022;28(1):162.
28.
Weigl M, Kocijan R, Ferguson J, et al. Longitudinal Changes of Circulating miRNAs During Bisphosphonate and Teriparatide Treatment in an Animal Model of Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res. 2021;36(6):1131–44.
29.
Gan L, Leng Y, Min J, et al. Kaempferol promotes the osteogenesis in rBMSCs via mediation of SOX2/miR-124-3p/PI3K/Akt/mTOR axis. Eur J Pharmacol. 2022;927:174954.
30.
Gu N, Wang Y, Li L, et al. The mechanism of lncRNA MALAT1 targeting the miR-124-3p/IGF2BP1 axis to regulate osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells. Clin Oral Investig. 2024;28(4):219.
31.
Li Z, Zhao H, Chu S, et al. miR-124-3p promotes BMSC osteogenesis via suppressing the GSK-3beta/beta-catenin signaling pathway in diabetic osteoporosis rats. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2020;56(9):723–34.
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.