Online first
Current issue
Archive
Special Issues
About the Journal
Publication Ethics
Anti-Plagiarism system
Instructions for Authors
Instructions for Reviewers
Editorial Board
Editorial Office
Contact
Reviewers
All Reviewers
2025
2024
2023
2022
2021
2020
2019
2018
2017
2016
General Data Protection Regulation (RODO)
RESEARCH PAPER
Effect of consumption of vegetables contaminated with pesticides on consumers’ health – risk analysis
1
Department of Public Health, Academy of Medical Sciences of Applied and Holistic Sciences, Warsaw, Poland
2
Department of Agronomy and Food Processing, Faculty of Agriculture and Biotechnology, University of Science and Technology, Bydgoszcz, Poland
3
Department of Environmental Chemistry and Risk Assessment, Institute of Environmental Protection/ National Research Institute, Warsaw, Poland
4
Faculty of Exact and Natural Sciences, University of the National Education Commission, Kraków, Poland
5
Department of Medical Anthropology, Institute of Rural Health, Lublin, Poland
Corresponding author
Magdalena Florek-Łuszczki
Department of Medical Anthropology, Institute of Rural Health, Lublin, Jaczewskiego 2, 20-090, Lublin, Poland
Department of Medical Anthropology, Institute of Rural Health, Lublin, Jaczewskiego 2, 20-090, Lublin, Poland
Ann Agric Environ Med. 2025;32(3):346-352
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction and objective:
The presence of pesticide residues in food is the consequence of the use of conventional methods of plant protection. The aim of the study was to assess health risk after consumption of the edible parts of vegetables (carrots, cucumbers, tomatoes) contaminated with pesticides.
Material and methods:
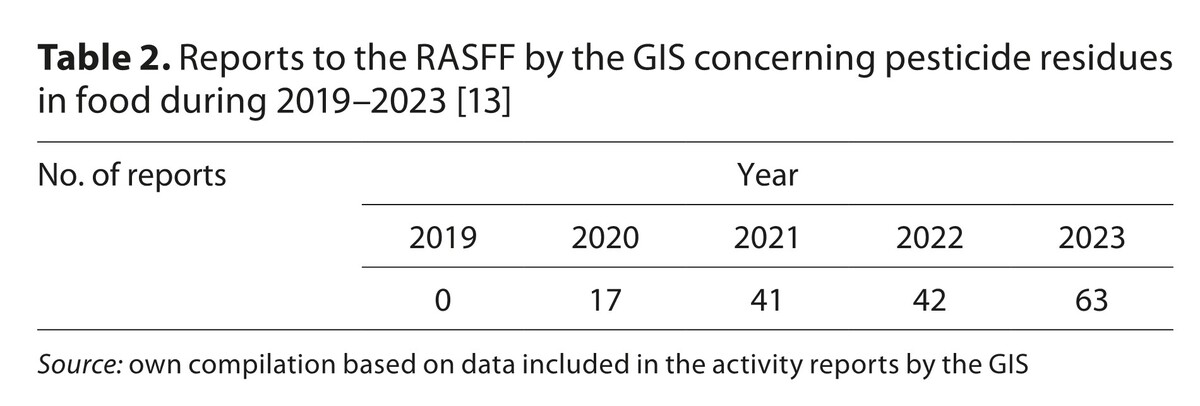
Research material was based on the results of pesticide residues in food available on the Polish market during 2019–2023. The volume of consumption of selected vegetables for the purposes of assessment of health risk was determined based on data from literature. In turn, data concerning the intake of daily doses of residues of harmful compounds after consumption of the selected vegetables were taken into account as part of the official control and monitoring carried out by the Chief Sanitary Inspectorate (GIS) reported by the National Institute of Public Health of the National Institute of Hygiene – National Research Institute (NIZP-PZH), and data from literature.
Results:
The calculated HI value indicates that no risk of occurrence of adverse health effects for consumers’ health should be expected, caused by the mixture of chemical substances after consumption of the analyzed vegetables.
Conclusions:
Contamination of plant foods with pesticides creates a serious risk for human health. Strict control of food is recommended starting with primary production through processing, storage, distribution, ending with consumption. To limit health risk resulting from exposure to pesticide residues while consuming vegetables, precautionary measures should be taken based on the application of good agricultural practices. The assessment of health risk caused by exposure to pesticides should be a permanent element of the activities of institutions responsible for food safety ‘from farm to fork’, especially those responsible for public health.
The presence of pesticide residues in food is the consequence of the use of conventional methods of plant protection. The aim of the study was to assess health risk after consumption of the edible parts of vegetables (carrots, cucumbers, tomatoes) contaminated with pesticides.
Material and methods:
Research material was based on the results of pesticide residues in food available on the Polish market during 2019–2023. The volume of consumption of selected vegetables for the purposes of assessment of health risk was determined based on data from literature. In turn, data concerning the intake of daily doses of residues of harmful compounds after consumption of the selected vegetables were taken into account as part of the official control and monitoring carried out by the Chief Sanitary Inspectorate (GIS) reported by the National Institute of Public Health of the National Institute of Hygiene – National Research Institute (NIZP-PZH), and data from literature.
Results:
The calculated HI value indicates that no risk of occurrence of adverse health effects for consumers’ health should be expected, caused by the mixture of chemical substances after consumption of the analyzed vegetables.
Conclusions:
Contamination of plant foods with pesticides creates a serious risk for human health. Strict control of food is recommended starting with primary production through processing, storage, distribution, ending with consumption. To limit health risk resulting from exposure to pesticide residues while consuming vegetables, precautionary measures should be taken based on the application of good agricultural practices. The assessment of health risk caused by exposure to pesticides should be a permanent element of the activities of institutions responsible for food safety ‘from farm to fork’, especially those responsible for public health.
REFERENCES (27)
1.
Jiang S, Wang F, Li Q, et al. Environment and food safety: a novel integrative review. Environ Sci Poll Res. 2021;28:54511–54530. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356....
2.
Gworek B, Baczewska-Dąbrowska AH, Kalinowski R, et al. Ecological risk assessment based on the TRIAD approach in an area contaminated by the metallurgical and mining industries. J Elem. 2024;29(1):99–121. http://doi.org/10.5601/jelem.2....
3.
Ochwanowska E, Czarny-Działak M, Żeber-Dzikowska I, et al. Chemicals in food as a health threat. Przem Chem. 2019;98(10):16141618.https://doi.org/10.15199/62.20... (in Polish).
4.
Dietrich GJ, Florek-Łuszczki M, Wojciechowska M, et al. Fish as bio-indicators of environmental pollutants and associated health risks to the consumer. J Elem. 2022; 27(4): 879–896. http://doi.org/10.5601/jelem.2....
5.
Philippe V, Neveen A, Marwa A, et al. Occurrence of pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables for the Eastern Mediterranean Region and potential impact on public health. Food Control. 2021;119: 107457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.food....
6.
Żeber-Dzikowska I, Gworek B, Goździewska M. Health risk resulting from pesticide residues in food of plant origin-a still valid challenge for health and ecological education. Annals of agricultural and environmental medicine: AAEM. 2025; 32(2), 274–279. https://doi.org/10.26444/aaem/....
7.
MacDonell MM, Hertzberg RC, Rice GE, et al. Characterizing Risk for Cumulative Risk Assessments. Risk Anal. 2018; 38(6):1183–1201. https://doi.org10.1111/risa.12....
8.
Lazarević-Pašti T, Milanković V, Tasić T, et al. With or Without You? A Critical Review on Pesticides in Food. Foods. 2025; 14(7):1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods1....
9.
Gwinn MR, Axelrad DA, Bahadori T, et al. Chemical Risk Assessment: Traditional vs Public Health Perspectives. Am J Public Health. 2017; 107(7):1032–1039. https://doi.org/10.2105/AJPH.2....
10.
Yang M, Wang Y, Yang G, et al. A review of cumulative risk assessment of multiple pesticide residues in food: Current status, approaches and future perspectives. Trends in Food Science & Technology. 2024;144,104340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs....
11.
Kosoń A, Chmielewski J, Szenk P, et al. Type of products selected and beverages consumed by primary school children. Health Probl Civilizat. 2024; https://doi.org/10.5114/hpc.20....
12.
EFSA 2022. The 2020 European Union Report on Pesticide Residues in Food. EFSA J. 2022;20,e07215. https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/....
14.
NIZP-PZH 2020, RAPORT: Analiza potencjalnego zagrożenia zdrowia konsumentów wynikającego z pozostałości pestycydów w żywności dostępnej na polskim rynku w roku 2020. https://www.pzh.gov.pl/raport-....
16.
Ssemugabo C, Bradman A, Ssempebwa JC, et al. An assessment of health risks posed by consumption of pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables among residents in the Kampala Metropolitan Area in Uganda. Food Contam. 2022;9:4. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40550....
17.
Davis CP, Garzia NA, Cushing-Haugen K, et al. Fruit and vegetable consumption, pesticide residue intake from consumption of fruits and vegetables, and risk of uterine fibroids. F S Sci. 2023;4(1):90–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xfss....
18.
da Silva TM, Seabra LMAJ, Colares LGT, et al. Risk assessment of pesticide residues ingestion in food offered by institutional restaurant menus. PloS One. 2024; 19(12): e0313836. https://doi.org/10.1371/journa....
19.
Tarmure S, Alexescu TG, Orasan O, et al. Influence of pesticides on respiratory pathology – a literature review. Ann Agric Environ Med. 2020;27(2):194–200. https://doi.org/10.26444/aaem/....
20.
Łozowicka B, Mojsak P, Jankowska M, et al. Toxicological studies for adults and children of insecticide residues with common mode of action (MoA) in pome, stone, berries and other small fruit. Sci Total Environ. 2016; 566: 144–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scit....
21.
Yang M, Wang Y, Yang G, et al. A review of cumulative risk assessment of multiple pesticide residues in food: Current status, approaches and future perspectives. Trends Food Sci Technol. 2024: 104340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs....
23.
Liang G, Gong W, Li B, et al. Analysis of heavy metals in foodstuffs and an assessment of the health risks to the general public via consumption in Beijing, China. Inter J Environ Res Public Health. 2019;16(6): 909. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph....
24.
Alengebawy A, Abdelkhalek ST, Qureshi SR, et al. Heavy metals and pesticides toxicity in agricultural soil and plants: Ecological risks and human health implications. Toxics. 2021; 9(3): 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics....
25.
Goutam Mukherjee A, Ramesh Wanjari U, Eladl MA, et al. Mixed Contaminants: Occurrence, Interactions, Toxicity, Detection, and Remediation. Molecules. 2022; 27(8): 2577. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecu....
26.
Yang Y, Yang M, Zhao T, et al. Residue and Risk Assessment of Fluopyram in Carrot Tissues. Molecules. 2022;. 27(17): 5544. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecu....
27.
El-Sheikh E-SA, Ramadan MM, El-Sobki AE, et al. Pesticide Residues in Vegetables and Fruits from Farmer Markets and Associated Dietary Risks. Molecules. 2022; 27(22):8072. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecu....
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.