Online first
Current issue
Archive
Special Issues
About the Journal
Publication Ethics
Anti-Plagiarism system
Instructions for Authors
Instructions for Reviewers
Editorial Board
Editorial Office
Contact
Reviewers
All Reviewers
2025
2024
2023
2022
2021
2020
2019
2018
2017
2016
General Data Protection Regulation (RODO)
RESEARCH PAPER
Application of biofilm community structure analysis for assessing the impact of a stormwater system on the aquatic environment
1
Department of Water Supply and Wastewater Disposal, Faculty of Environmental Engineering and Energy, Lublin University of Technology, Lublin, Poland
2
Department of Applied Mathematics, Faculty of Mathematics and Information Technology, Lublin University of Technology, Lublin, Poland
3
Department of Natural Environment Biogeochemistry, Institute of Agrophysics, Polish Academy of Sciences, Lublin, Poland
4
Department of Technical Computer Science, Faculty of Mathematics and Information Technology, Lublin University of Technology, Lublin, Poland
5
Department of Invertebrate Fauna and Systematics, National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine, Kyiv, Ukraine
6
Department of Toxicology and Food Safety, Institute of Rural Health, Lublin, Poland
Corresponding author
Magdalena Piłat-Rożek
Department of Applied Mathematics, Faculty of Mathematics and Information Technology, Lublin University of Technology (20-618 Lublin, Poland), Nadbystrzycka 38, 20-618, Lublin, Poland
Department of Applied Mathematics, Faculty of Mathematics and Information Technology, Lublin University of Technology (20-618 Lublin, Poland), Nadbystrzycka 38, 20-618, Lublin, Poland
Ann Agric Environ Med. 2025;32(4):461-468
KEYWORDS
surface waterperiphytonbioindicationaquatic environmentcommunity structurestormwater systementropy-based indices
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction and objective:
Industrial, agricultural and construction development has brought improvements in living conditions, but have also increased the amount of pollution in the environment. Atmospheric precipitation collects pollutants from urban surfaces, which then end up in stormwater systems, contaminating surface waters. These pollutants are also linked to the similar effects of agriculture, as biogenic pollutants originate from over-fertilized crops. Contaminated surface water forces flora and fauna to adapt to new conditions, and affecting the structure and extent of ecosystems. Monitoring the environment with bio-indication methods is important because it enables identification of the areas in need of protection, in an inexpensive and environmentally harmless way. The aim of this study was to evaluate the possibility of using biocenotic indices to assess the impact of a stormwater system on the aquatic environment.
Material and methods:
Bio-indicative studies were conducted on periphyton sampled at 4 points on the Bystrzyca River in Lublin, eastern Poland, under the influence of stormwater discharge and 1 reference point localized before the stormwater system outflow. The quantitative data concerning the number of chosen algae species was analyzed using indices for the examination of community structure.
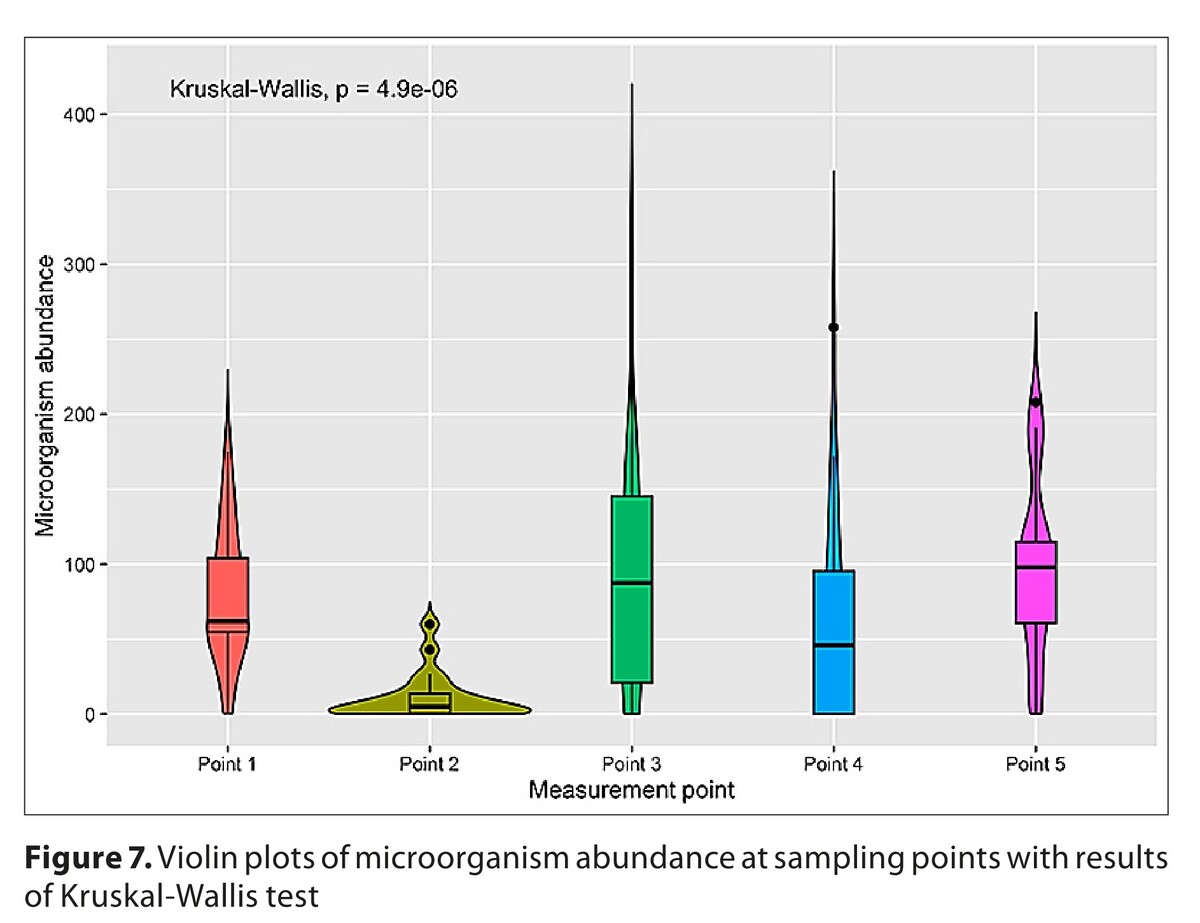
Results:
Considered the indices, i.e. taxonomic richness, Shannon, MacArthur, Menhinick and McIntosh were calculated, evaluated, and shown in various types of graphs showing the fluctuation of indices at measurement points.
Conclusions:
The use of bioindication and classic biocenotic indices allowed for the description, analysis of changes in the periphyton biocenosis under the influence of point source stormwater discharges, and linking measurements from tested samples with environmental conditions and biodiversity in the analyzed study sites and periods.
Industrial, agricultural and construction development has brought improvements in living conditions, but have also increased the amount of pollution in the environment. Atmospheric precipitation collects pollutants from urban surfaces, which then end up in stormwater systems, contaminating surface waters. These pollutants are also linked to the similar effects of agriculture, as biogenic pollutants originate from over-fertilized crops. Contaminated surface water forces flora and fauna to adapt to new conditions, and affecting the structure and extent of ecosystems. Monitoring the environment with bio-indication methods is important because it enables identification of the areas in need of protection, in an inexpensive and environmentally harmless way. The aim of this study was to evaluate the possibility of using biocenotic indices to assess the impact of a stormwater system on the aquatic environment.
Material and methods:
Bio-indicative studies were conducted on periphyton sampled at 4 points on the Bystrzyca River in Lublin, eastern Poland, under the influence of stormwater discharge and 1 reference point localized before the stormwater system outflow. The quantitative data concerning the number of chosen algae species was analyzed using indices for the examination of community structure.
Results:
Considered the indices, i.e. taxonomic richness, Shannon, MacArthur, Menhinick and McIntosh were calculated, evaluated, and shown in various types of graphs showing the fluctuation of indices at measurement points.
Conclusions:
The use of bioindication and classic biocenotic indices allowed for the description, analysis of changes in the periphyton biocenosis under the influence of point source stormwater discharges, and linking measurements from tested samples with environmental conditions and biodiversity in the analyzed study sites and periods.
FUNDING
Polish Ministry of Education and Science within Grant Nos. FN-38, FD-20/IS-6/021.
REFERENCES (25)
1.
Widomski M, Musz-Pomorska A. Zielona architektura i zagospodarowanie wody opadowej jako element strategii przeciwdziałania zmianom klimatycznym na obszarach zurbanizowanych. In: Kowalska B, editor. Wpływ zmian klimatu na gospodarkę wodno-ściekową w aspekcie bezpieczeństwa zdrowotnego wody. Wydawnictwo Polskiej Akademii Nauk; 2021. p. 199–222.
2.
Januchta-Szostak A. Zarządzanie wodami opadowymi w miastach. Wodociągi – Kanalizacja. 2019;9:22–24.
3.
Numberger D, Ganzert L, Zoccarato L, et al. Characterization of bacterial communities in wastewater with enhanced taxonomic resolution by full-length 16S rRNA sequencing. Sci Rep. 2019;9:9673. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598....
4.
Gorzel M, Kornijów R, Buczyńska E. Quality of rivers: comparison of hydro-morphological, physical-chemical and biological methods. Ecological Chemistry and Engineering S. 2018;25(1):101–22.
5.
Gajewska M. Złoża hydrofitowe z pionowym przepływem ścieków charakterystyka procesów i zastosowań. Polska Akademia Nauk, 2019.
6.
Babko R, Szulżyk-Cieplak J, Danko Y, et al. Evaluation of Stormwater System Influence on the River Using Algae. J Ecol Engineering. 2020;21(2):214–21. https://doi.org/10.12911/22998....
7.
Babko R, Szulżyk-Cieplak J, Danko Y, et al. Effect of Stormwater System on the Receiver. J Ecol Engineering. 2019;20(6):52–59.
8.
Łagód G. Bioindykacja w kontroli procesu oczyszczania ścieków. Polska Akademia Nauk, 2017.
9.
Bondaruk J, Janson E, Wysocka M, et al. Identification of hazards for water environment in the Upper Silesian Coal Basin caused by the discharge of salt mine water containing particularly harmful substances and radionuclides. J Sustain Min. 2015;14(4):179–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsm.....
10.
Ma F, Wang C, Zhang Y, et al. Development of microbial indicators in ecological systems. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(21):13888. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph....
11.
Sumudumali R, Jayawardana J. A review of biological monitoring of aquatic ecosystems approaches: with special reference to macroinvertebrates and pesticide pollution. Environ Manage. 2021;67(2):263–276. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267....
12.
Oksanen J, Simpson G, Blanchet F, et al. Vegan: community ecology package. 2025. https://vegandevs.github.io/ve... (access: 2025.09.20).
13.
Mulya H, Santosa Y, Hilwan I. Comparison of four species diversity indices in mangrove community. Biodiversitas. 2021;22(9):3648–55. https://doi.org/10.13057/biodi....
14.
Thukral AK. A review on measurement of Alpha diversity in biology. Agric Res J. 2017;54(1):1. https://doi.org/10.5958/2395-1....
15.
Bollarapu M, Kuchibhotla S, Kvsn R, et al. Dynamic perspectives on biodiversity quantification: beyond conventional metrics. Peer J. 2024;12:e17924. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.....
16.
Tareen A, Nadeem M, Kearfott K, et al. Descriptive analysis and earthquake prediction using boxplot interpretation of soil radon time series data. Appl Radiat Isot. 2019;154:108861. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apra....
17.
Colonval J, Bouquet F. Hunting Inside N-Quantiles of Outliers (Hino). In: Wu X, Spiliopoulou M, Wang C, et al. Data Science: Foundations and Applications. PAKDD 2025. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Springer, Singapore. 2025;15875. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-98....
18.
Richardson J. Kruskal–Wallis Test. In: Frey B, editor. The SAGE Encyclopedia of Educational Research, Measurement, and Evaluation. SAGE Publications, Inc; 2018. p. 937–939. https://doi.org/10.4135/978150....
19.
Bartkowska A, Chmiel D, Sise R, et al. Kolonizacja potencjalnych materiałów dowodowych przez makrofaunę bezkręgową w rzece Bystrzycy. In: Babicz M, Nowakowicz-Dębek B, Kropiwiec-Domańska K, editors. Wybrane zagadnienia z zakresu ochrony i zagrożeń środowiska Tom 2. Uniwersytet Przyrodniczy w Lublinie; 2022. p. 7–15.
20.
Sender J, Grabowski M, Urban D, et al. Preliminary study of water quality improving in storage reservoir by introducing of artificial phytolittoral. Annual Set The Environment Protection. 2018;20:392–416.
21.
Kozłowska A, Wojtaś E, Piłat-Rożek M, et al. Analysis of the Impact of Stormwater Systems on Receiving Waters Based on the Analysis of Algal Community Structure. J Ecol Engineering. 2023;24(9):139–47. https://doi.org/10.12911/22998....
22.
Nawrot N, Wojciechowska E. Review on the quality of sediments from the stormwater drainage system in the urban area. E3S Web Conf. 2017;17:00064. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3scon....
23.
Bąk M, Witkowski A, Żelazna-Wieczorek J, et al. Klucz do oznaczania okrzemek w fitobentosie na potrzeby oceny stanu ekologicznego wód powierzchniowych w Polsce. Główny Inspektorat Ochrony Środowiska. 2012. https://doi.org/10.13140/2.1.3....
24.
Czerpak J, Bomba B. Skład chemiczny śniegu miasta Lublin jako indykator zanieczyszczenia środowiska. In: Pilarska A, Pilarski K, editors. Nowoczesne rozwiązania w ochronie środowiska. Zagadnienia wybrane. Wydawnictwo Naukowe TYGIEL; 2023. p. 107–27.
25.
Mencwel J. Betonoza. Jak się niszczy polskie miasta. Wydawnictwo Krytyki Politycznej; 2020.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.