Online first
Current issue
Archive
Special Issues
About the Journal
Publication Ethics
Anti-Plagiarism system
Instructions for Authors
Instructions for Reviewers
Editorial Board
Editorial Office
Contact
Reviewers
All Reviewers
2025
2024
2023
2022
2021
2020
2019
2018
2017
2016
General Data Protection Regulation (RODO)
CASE REPORT
Severe carbamates intoxication of 43-year-old farmer – case report
1
Toxicology Clinic, Medical University, Lublin, Poland
2
Clinical Department of Toxicology and Cardiology, Stefan Wyszyński Regional Specialist Hospital, Lublin, Poland
Corresponding author
Ann Agric Environ Med. 2021;28(2):358-360
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
Carbamate insecticides are methyl carbamic acid esters and reversible cholinesterase inhibitors. In contrast to the long-term action of organophosphate insecticides, this complex undergoes rapid hydrolysis.
Case report:
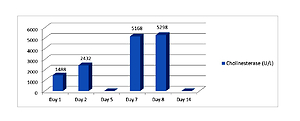
A suicidal poisoning by exposure to carbofuran in a 43-year-old farmer is reported. The patient had a sudden respiratory and cardiac arrest in the mechanism of bradycardia asystole. He was additionally diagnosed with metabolic acidosis and massive aspiration pneumonia. After applied treatment, the patient’s general condition improved – alignment of efficiency of both respiratory and circulatory efficiency were reached.
Conclusion:
Carbofuran is one of the most toxic carbamate insecticides. It is therefore important to react quickly and choose the right treatment. Differentiation between organophosphate and carbamate intoxication is essential.
Carbamate insecticides are methyl carbamic acid esters and reversible cholinesterase inhibitors. In contrast to the long-term action of organophosphate insecticides, this complex undergoes rapid hydrolysis.
Case report:
A suicidal poisoning by exposure to carbofuran in a 43-year-old farmer is reported. The patient had a sudden respiratory and cardiac arrest in the mechanism of bradycardia asystole. He was additionally diagnosed with metabolic acidosis and massive aspiration pneumonia. After applied treatment, the patient’s general condition improved – alignment of efficiency of both respiratory and circulatory efficiency were reached.
Conclusion:
Carbofuran is one of the most toxic carbamate insecticides. It is therefore important to react quickly and choose the right treatment. Differentiation between organophosphate and carbamate intoxication is essential.
REFERENCES (8)
1.
Eddleston M, Clark RF. Insecticides: Organic phosphorus compounds and carbamates, p.1409–1420; Howland MA. Atropine, p. 1425–1428 in: Hoffmann R, Howland M, Lewin N, Nelson L, Goldfrank L, Wiener S. Goldfrank’s Toxicologic Emergencies, Tenth Edition Copyright 2015 by McGraw-Hill Education.
3.
Gawlikowski T, Hubalewska-Dydejczyk A, Pach D. Acute suicidal carbofuran poisoning – case report. Przegl Lek. 2007; 64(4–5): 322–3.
4.
Clark RF. Anticholinesterase (organic phosphorus carbamate) pesticide poisoning. California poison control system https://calpoison.org/news/ant... (access: 2019.06.15).
5.
Silberman J, Taylor A. Carbamate Toxicity. [Updated 2018 Oct 27]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): 2019 Jan.
6.
Seńczuk W, editors. Toksykologia. Podręcznik dla studentów, lekarzy i farmaceutów. 4th ed. Warsaw: Wydawnictwo Lekarskie PZWL; 2002, p.500–502.
7.
Panasiuk L, Król M, Szponar E, Szponar J, editors. Ostre zatrucia, Wydawnictwo Lekarskie PZWL; 2009, p. 100.
8.
Brenner GM, Stevens CW. Acetylocholine receptor agonists. Pharmacology 2010, p. 71.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.